
Fiber Patch Cord
What is a Fiber Patch Cord and How it Works?
A fiber patch cord, also known as a fiber patch cable or fiber jumper, is an essential component in fiber optic networks. It acts as a link that connects various optical devices, such as switches, routers, and transceivers, enabling the transmission of optical signals between them.
Fiber patch cords work on the principle of total internal reflection, where light signals propagate through a fiber optic cable. The core of a fiber patch cord consists of one or more optical fibers, which are extremely thin strands made of glass or plastic. These fibers are designed to carry light signals over long distances with minimal loss.
When a fiber patch cord is connected, the fiber connectors at each end align and mate securely with the corresponding connectors on the devices being connected. The alignment is crucial to ensure that the optical signals pass through the fibers without significant loss or distortion.
Inside the connectors, the tiny fiber cores are precisely aligned to maintain the integrity of light transmission. The cores have a higher refractive index than the cladding surrounding them, causing light signals to be continuously reflected within the fiber core as they travel along it. This phenomenon, known as total internal reflection, allows the light signals to propagate through the fiber without leaking out.
The fiber patch cord acts as a bridge, transmitting optical signals from one device to another. It provides a reliable and efficient means of communication, enabling high-speed data transmission, voice communication, and video streaming over fiber optic networks.
Tailored Fiber Patch Cord Solution from FMUSER
At FMUSER, we take pride in crafting custom-made Fiber Optic Patch Cables that surpass expectations. Our highly trained technicians in China meticulously handcraft each cable, ensuring unmatched quality that's built to last. When it comes to your specific installation needs, we have you covered.
Why FMUSER?
Here are our advantages ober other patch cord manufacturers:
- A Seamless Experience from Start to Finish: From the moment you place your order, we prioritize your satisfaction. We keep you informed every step of the way, providing an immediate order confirmation. Rest assured that your custom cables will be shipped within 24 hours, and we'll even provide you with tracking information to keep you in the loop as your cables make their way to you.
- Uncompromising Quality Guaranteed: At FMUSER, we believe in delivering nothing short of excellence. Our Fiber Optic Patch Cables are meticulously manufactured alongside our custom fiber optic distribution assemblies, ensuring consistent premium components and rigorous quality control. We use high-quality glass and premium connectors with ceramic ferrules, offering enhanced durability and accuracy that you can rely on.
- Performance and Precision Tested: Our Fiber Optic Patch Cables undergo rigorous testing to guarantee top performance. With a maximum allowable insertion loss of 0.02 dB or less, you can trust that our cables deliver unparalleled connectivity. Each connector is meticulously inspected under a 400x microscope, detecting even the smallest surface or interior defects that may impact performance.
- Versatile and Safe: Designed for critical installations, our Fiber Optic Patch Cables feature a 2mm plenum (OFNP) rated jacket, making them suitable for all indoor environments. Unlike regular riser-rated (OFNR) or standard PVC cables found in stock patch cables, our plenum-rated cables surpass industry standards by ensuring low-smoke characteristics as defined by the NFPA (National Fire Protection Agency).
- Quality Assurance and Peace of Mind: At FMUSER, we stand by the reliability and performance of our Fiber Optic Patch Cables. Each cable comes with a test report and undergoes full testing to meet our stringent quality standards. We ensure easy identification and traceability by labeling each cable with a unique serial number and part number. With individual packaging and accompanying test results, you can have full confidence in your FMUSER Fiber Optic Patch Cables.
- Choose FMUSER for Exceptional Fiber Optic Patch Cables: Our dedication to quality control is evident through our ISO9000 certification. With FMUSER, you can trust that your custom-made Fiber Optic Patch Cables are crafted with precision and attention to detail. Experience the FMUSER difference and elevate your connectivity to new heights.
Factory Price, In-stock & Ship the Same Day
At FMUSER, we not only offer exceptional customization options for your Fiber Optic Patch Cable but also provide an unbeatable price advantage. As a factory-direct sales provider, we eliminate unnecessary intermediaries, providing competitive factory prices while maintaining uncompromising quality.

Whether you need a single custom cable or require wholesale orders, our pricing structure is designed to meet your needs. Take advantage of our attractive discounts for bulk purchases, ensuring cost-effective solutions without compromising performance.
But that's not all – we understand the importance of timely delivery. With our commitment to customer satisfaction, we have a wide range of in-stock options available. This means that when you place your order, we are ready to ship it out today, ensuring swift delivery right to your doorstep. No more waiting for weeks – get the cables you need promptly and efficiently.
Choose FMUSER for unbeatable prices, factory-direct sales, exclusive wholesale discounts, and the added convenience of in-stock availability. Experience the perfect blend of affordability, customization, and immediate shipping options for a seamless purchasing experience.
Customization at its Finest
Our turnkey fiber patch cord solutions empower you to personalize every aspect of your Fiber Optic Patch Cable. From choosing the perfect length, ranging from a concise 6 inches to an impressive 30 meters, to offering a diverse range of connector types such as the popular LC, SC, and ST connectors. Our goal is to seamlessly connect your fiber optic enclosures to SPF transceivers, network switches, or media converters, ensuring effortless compatibility

Explore the array of customization options available to tailor your fiber optic experience with FMUSER:
- Boot Color & Length: Customized according to your preferences.
- Cable Color: Customized to suit your needs.
- Cable OD: Customized options available, including 2.0mm and 3.0mm.
- Cable Printing: Customizable for labeling or branding purposes.
- Length: Customized to meet your specific requirements.
- Individual PE Bag with Sticky Label Report: Each patch cord is packaged in an individual PE bag with a sticky label report for easy identification and organization.
- Customer Logo Printing: We can print your logo on labels for branding purposes.
- and more (welcome to contact us)
Connector Types & Polishing: Highly Precision
At FMUSER, we understand that different applications demand specific connector types and polishing options to achieve optimal performance. That's why we offer a diverse range of connector types and polishing choices to accommodate your unique requirements.
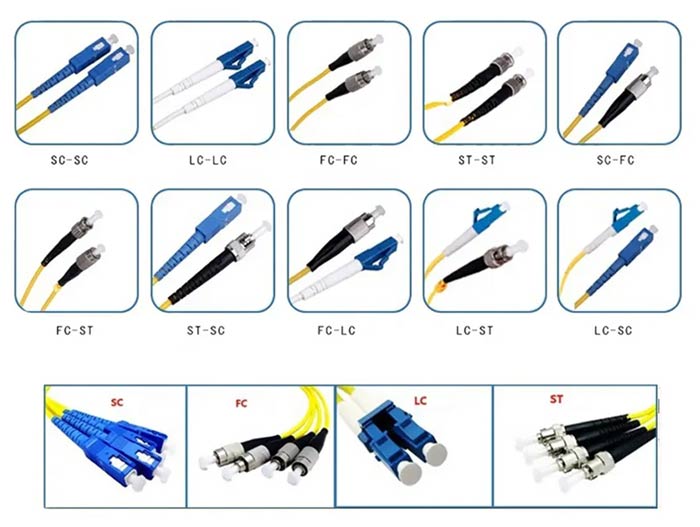
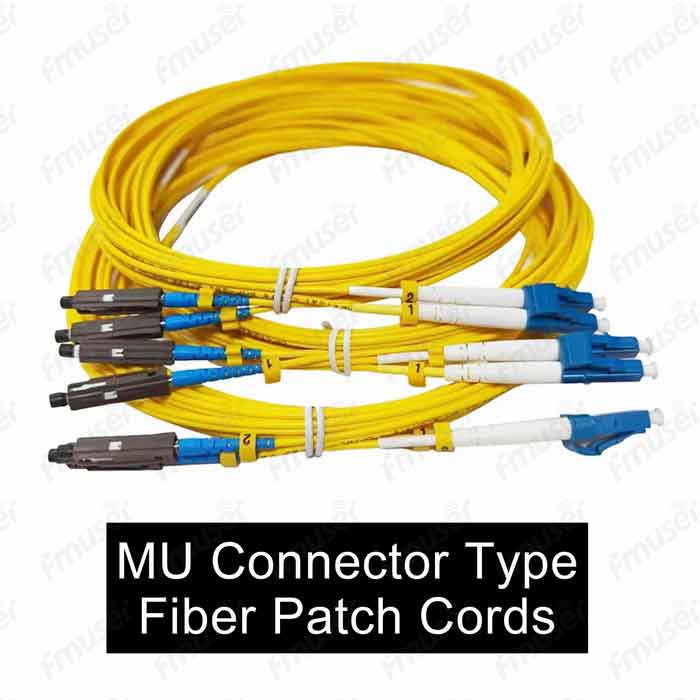
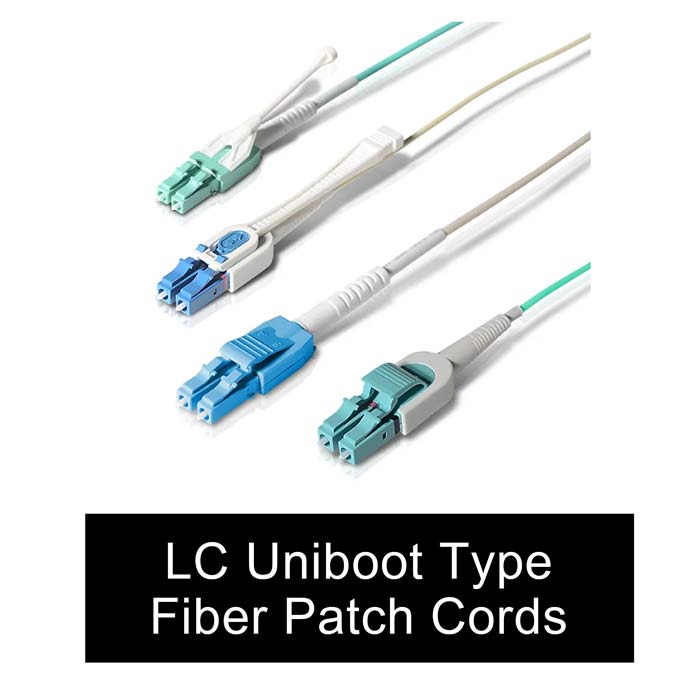
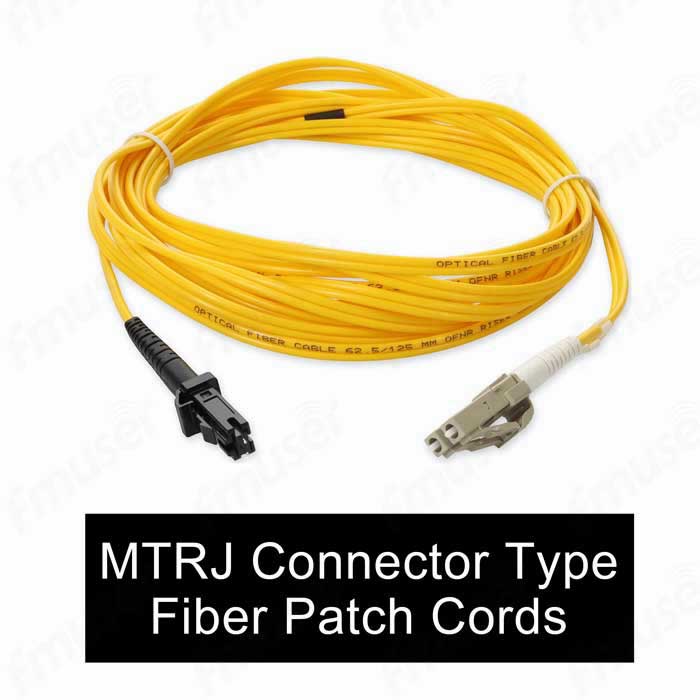
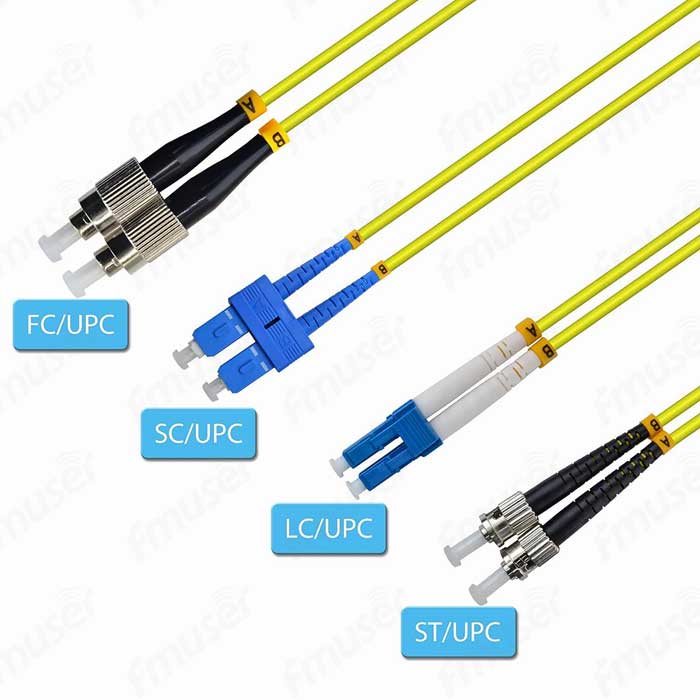
1. Connector Types: Our extensive selection includes popular connector types like FC, SC, ST, LC, MU, MT-RJ, E2000, SMA, and more. Whether you need a robust connector for high-vibration environments or a compact connector for dense installations, we have the perfect solution to meet your connectivity needs.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| LC Uniboot Fiber Patch Cords Series | MTRJ Fiber Patch Cords Series | SMA Fiber Patch Cords Series |
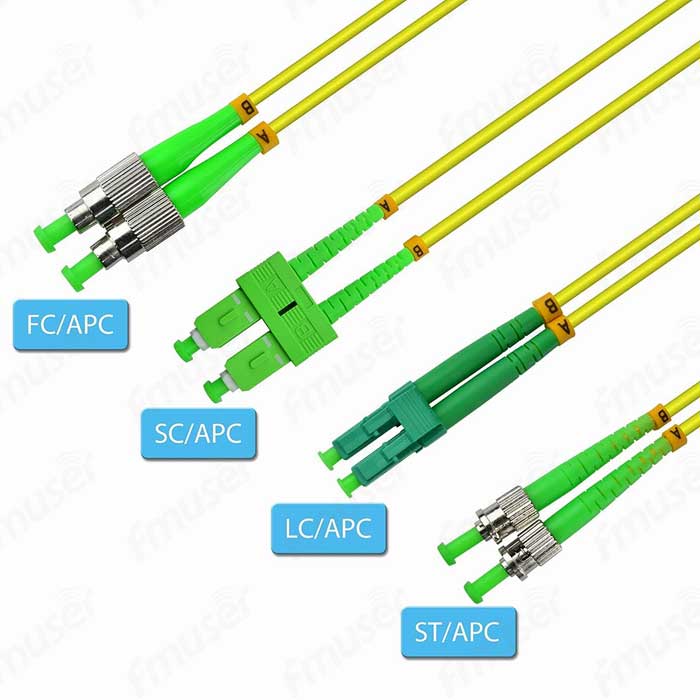
2. Polish Types: We recognize the importance of precision in fiber optic connections. Therefore, we offer different polish types to ensure maximum signal integrity. Choose from PC (Physical Contact), UPC (Ultra Physical Contact), and APC (Angled Physical Contact) polish options. Each polish type offers specific benefits, allowing you to achieve the level of performance required for your application.
 |
 |
| UPC Polishing | APC Polishing |
With our comprehensive range of connector types and polishing options, you have the flexibility to create custom Fiber Optic Patch Cables that perfectly align with your unique specifications. Trust FMUSER to provide the versatility and precision needed to optimize your fiber optic connections.
Patch Cord and Pigtail Options: Versatility for Every Need
To ensure seamless connectivity for different applications, we supply a wide range of patch cord and pigtail options:
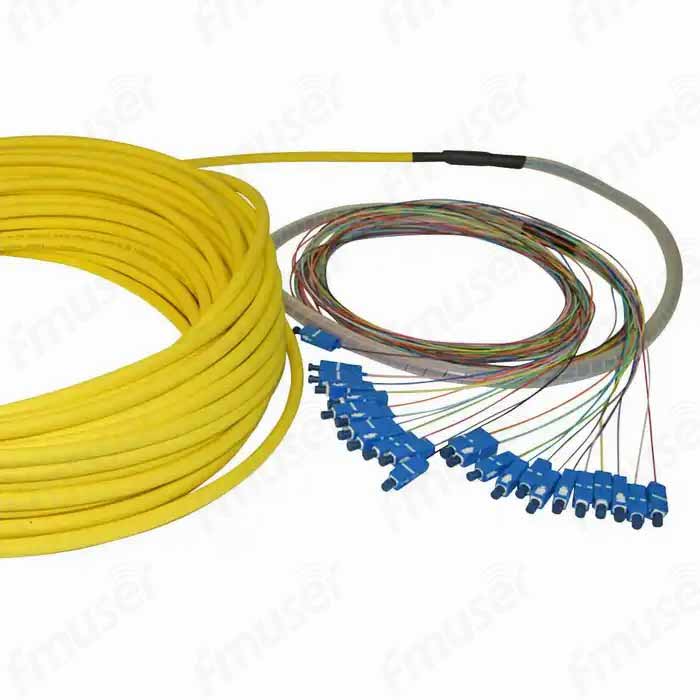
1. Simplex, Duplex, or Multi-fiber: Choose the configuration that best suits your requirements. Whether you need a simplex patch cord for one-way communication, a duplex patch cord for bidirectional data transmission, or a multi-fiber option for applications demanding multiple connections, we have the perfect solution for you. Our patch cords and pigtails are available in various configurations to cater to standard or customized applications.

2. SM/MM Patch Cord and Pigtails: We provide both single mode (SM) and multimode (MM) options to align with your specific fiber type requirements. Whether you need a patch cord or pigtail for long-distance data transmission (SM) or for shorter distances within a local area network (MM), our comprehensive range ensures that you find the ideal solution.
 |
 |
 |
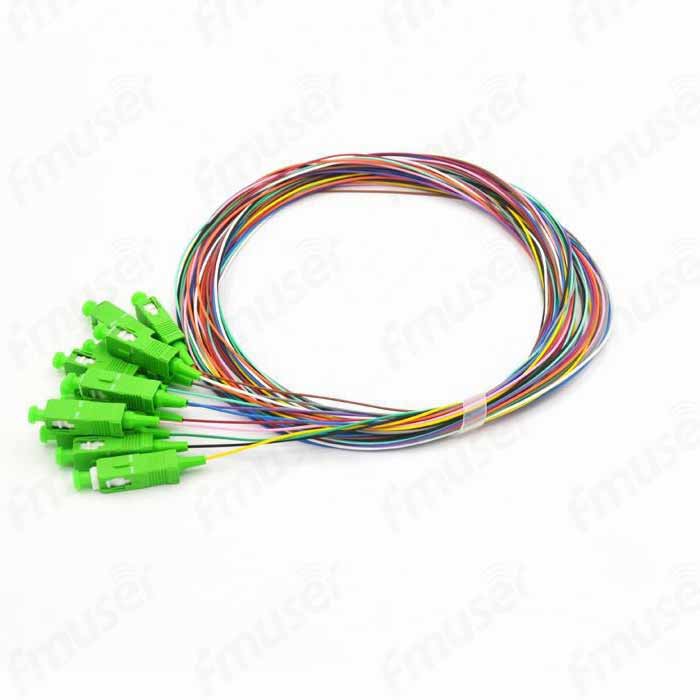 |
At FMUSER, we prioritize versatility and customization to meet your unique patch cord and pigtail needs. Choose from a wide range of configurations and fiber types, and experience reliable and efficient connectivity tailored to your exact requirements.
Cable Specifications: Tailored to Your Requirements
Since every fiber optic installation is unique, you can find any cable specifications catering to your specific needs.

- Cable Diameter: Choose from various cable diameters, including options such as 0.9mm, 2.0mm, or 3.0mm. This allows you to select the ideal cable diameter that suits your application, providing flexibility and ease of installation.
- Length/Type: We are committed to providing patch cords and pigtails according to your specific demands. Whether you require standard lengths or customized cable lengths, we can accommodate your requirements, ensuring a seamless fit within your network infrastructure.
- Jacket Types: Our cable offerings include PVC, LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen), and PE jacket options. You can select the appropriate jacket type based on your environmental and safety considerations, ensuring compliance with regulations and the specific requirements of your installation.
- Custom Fiber Optic Cable Lengths and Jacket Colors: At FMUSER, we understand the desire for customization. That's why we can accommodate custom lengths and jacket colors to match your specific preferences. With our tailored approach, your fiber optic cables can be unique to your installation, allowing for easy identification and seamless integration into your network setup.
Can't find what you need? Just ask! We're here to help.
With our wide range of cable specifications, FMUSER ensures that your fiber optic patch cords and pigtails are tailored precisely to your requirements. Choose the cable diameter, length/type, jacket type, and even customize the cable lengths and jacket colors, all to create a solution that perfectly aligns with your needs. Experience the power of customization with FMUSER.
Fiber Types and Wavelengths: Catering to Your Connectivity
We also offer support for various fiber types and wavelengths, ensuring that our fiber optic patch cords and pigtails are tailored to your specific needs. This versatility allows us to provide you with the flexibility and performance required for your unique connectivity requirements.
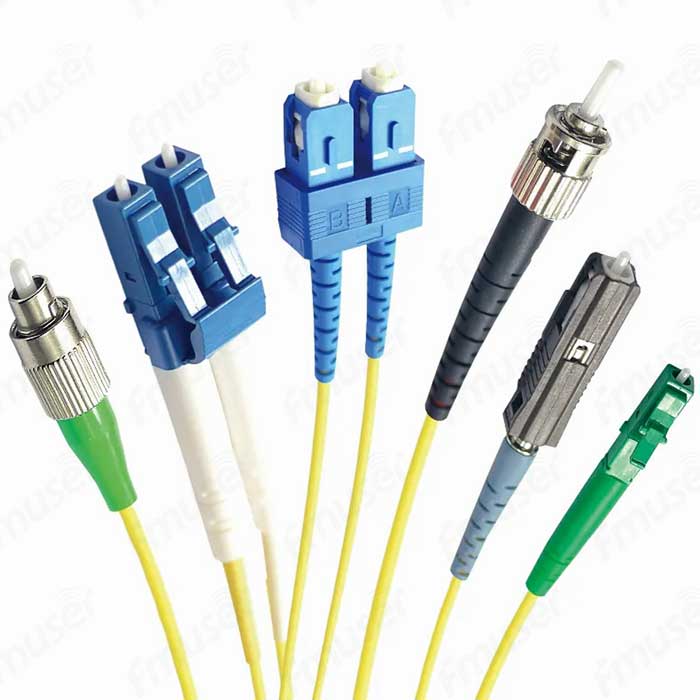

Typical Fiber Types:
- 9/125 Single Mode Fiber: Ideal for long-distance transmissions, this fiber type offers a narrow core size and supports a single light mode, enabling high-speed data transfer over extended distances.
- 50/125 Multimode Fiber: Suitable for shorter-range applications, this fiber type has a larger core size, allowing multiple light modes to propagate simultaneously. It is commonly used for local area networks (LANs) and other applications where shorter distances are involved.
- 62.5/125 Multimode Fiber: Although less commonly used today, this fiber type also supports multimode transmission over shorter distances.
By providing support for these typical fiber types, we ensure that our fiber optic patch cords and pigtails are compatible with a wide range of applications and network setups.
Wavelengths:
In addition to supporting various fiber types, we also accommodate different wavelengths that are commonly used in fiber optic communications, including 850nm, 1310nm, and 1550nm. These wavelength options allow us to optimize the performance and efficiency of your fiber optic connections, delivering reliable and high-speed data transmission.
At FMUSER, we are committed to providing you with the flexibility and performance you need for your fiber optic installations. Our support for different fiber types and wavelengths ensures that your fiber optic patch cords and pigtails are customized to meet your specific requirements, enabling seamless connectivity and optimal data transfer.
Now, let's explore the wide range fiber patch cord options from FMUSER!
-
![SMA-905/906 Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today]()
SMA-905/906 Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:14
-
![MTRJ Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today]()
MTRJ Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:14
-
![LC Uniboot Patch Cord Fiber | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today]()
LC Uniboot Patch Cord Fiber | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:14
-
![E2000 Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today]()
E2000 Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:14
-
![MU Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today]()
MU Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:14
-
![FC Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today]()
FC Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:14
-
![ST UPC Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today]()
ST UPC Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:14
-
![LC Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today]()
LC Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:14
-
![SC Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today]()
SC Fiber Patch Cord | Custom Length, DX/SX, SM/MM, In Stock & Ship Same Today
Price(USD):Ask for a quotation
Sold:14
- How many types of fiber patch cords are there?
-
There are several types of fiber patch cords commonly used in telecommunications and network applications. Here are some of the most common types:
- Single-mode patch cords (OS1/OS2): These patch cords are designed for long-distance transmission over single-mode fiber optic cables. They have a smaller core size (9/125µm) compared to multi-mode patch cords. Single-mode patch cords offer higher bandwidth and lower attenuation, making them suitable for long-range communication.
- Multi-mode patch cords (OM1/OM2/OM3/OM4/OM5): Multi-mode patch cords are used for short-distance transmissions within buildings or campuses. They have a larger core size (50/125µm or 62.5/125µm) compared to single-mode patch cords. The different types of multi-mode patch cords, such as OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5, have varying bandwidth and transmission capabilities. OM5, for example, supports higher speeds and longer distances compared to OM4.
- Bend-insensitive patch cords: These patch cords are designed to withstand tighter bending radii without experiencing signal loss. They are commonly used in areas where fiber cables need to be routed through tight spaces or around corners.
- Armored patch cords: Armored patch cords have an additional layer of protection in the form of metal armoring surrounding the fiber optic cable. The armor provides enhanced durability and resistance to external factors, making them suitable for harsh environments or areas prone to physical damage.
- Hybrid patch cords: Hybrid patch cords are used to connect different types of fiber optic cables or connectors. They allow for the conversion or connection of different fiber types, such as single-mode to multi-mode or SC to LC connectors.
It's important to note that there may be additional specialized types of fiber patch cords available for specific applications or niche requirements. When selecting a fiber patch cord, factors such as transmission distance, bandwidth requirements, environmental conditions, and connector compatibility should be considered.
- What is the purpose of a fiber optic patch cord?
-
The purpose of a fiber optic patch cord is to establish a temporary or permanent connection between optical devices, such as transceivers, switches, routers, or other networking equipment. It allows for the transmission of data signals through fiber optic cables. Here is an overview of the common purposes of fiber patch cords:
- Interconnecting network equipment: Fiber patch cords are essential for connecting various network devices within a data center, local area network (LAN), or wide area network (WAN). They provide a reliable and high-speed link for data transmission between devices.
- Extending network reach: Patch cords are used to extend the reach of optical connections. They can be used to connect devices within the same rack or across different racks or cabinets in a data center.
- Connecting to the outside world: Fiber patch cords enable connections between network equipment and external networks, such as Internet Service Providers (ISPs) or telecommunications providers. They are commonly used to connect routers or switches to outside network interfaces.
- Supporting different fiber types: Depending on the type of fiber optic cable being used (single-mode or multi-mode), different patch cords are required. Single-mode patch cords are designed for long-distance transmissions, while multi-mode patch cords are suitable for shorter distances.
- Facilitating high-speed data transmission: Fiber patch cords are capable of transmitting data at high speeds, making them ideal for applications that require high bandwidth, such as video streaming, cloud computing, or data centers.
- Enabling flexibility and scalability: Patch cords provide flexibility in network configurations, allowing for easy addition, removal, or rearrangement of devices within a network. They support scalability by accommodating changes and upgrades in network infrastructure.
It's important to select the appropriate type of fiber patch cord based on the specific requirements of the network, such as transmission distance, bandwidth, and overall performance needs.
- What are the components of a fiber optic patch cord?
-
A fiber optic patch cord typically consists of several components that work together to ensure reliable and efficient data transmission. Here are the common components found in a fiber optic patch cord:
- Fiber optic cable: The cable itself is the central component of a patch cord and is responsible for transmitting the optical signals. It consists of one or more optical fibers enclosed in a protective jacket.
- Connector: The connector is attached to each end of the fiber optic cable and is responsible for establishing the connection with other optical devices. Common connector types include LC, SC, ST, and FC.
- Ferrule: The ferrule is a cylindrical component inside the connector that holds the fiber securely in place. It is usually made of ceramic, metal, or plastic and ensures precise alignment between fibers when connected.
- Boot: The boot is a protective covering that surrounds the connector and provides strain relief. It helps prevent damage to the fiber and ensures a secure connection.
- Housing: The housing is the outer casing that protects the connector and provides stability. It is commonly made of plastic or metal.
In addition to these common components, different types of fiber patch cords may have unique components based on their specific purpose or design. For example:
- Bend-insensitive patch cords: These patch cords may have a special fiber construction designed to reduce signal loss when bent at tighter radii.
- Armored patch cords: Armored patch cords feature an additional layer of metal armor for added protection against physical damage or harsh environments.
- Hybrid patch cords: Hybrid patch cords may have components that allow for the conversion or connection between different fiber types or connector types. It's important to note that while the core components of a fiber optic patch cord remain consistent, specialized types may have additional features or modifications to meet specific requirements or environmental conditions.
- What types of connectors are used in fiber patch cords?
-
Fiber patch cords use different types of connectors to establish connections between optical devices. Each connector has its unique characteristics, structure, and applications. Here are some common types of fiber patch cord connectors:
- LC Connector: The LC (Lucent Connector) is a small form-factor connector widely used in high-density environments. It has a push-pull design and features a 1.25mm ceramic ferrule. LC connectors are known for their low insertion loss and compact size, making them suitable for data centers, LANs, and fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) applications.
- SC Connector: The SC (Subscriber Connector) is a popular connector used in telecommunications and data communication networks. It features a square-shaped 2.5mm ceramic ferrule and a push-pull mechanism for easy insertion and removal. SC connectors are commonly used in LANs, patch panels, and equipment connections.
- ST Connector: The ST (Straight Tip) connector was one of the first connectors widely used in fiber optic networks. It features a bayonet-style coupling mechanism and uses a 2.5mm ceramic or metal ferrule. ST connectors are commonly used in multimode networks, such as LANs and premises cabling.
- FC Connector: The FC (Ferrule Connector) is a threaded connector widely used in telecommunication and test environments. It features a screw-on coupling mechanism and uses a 2.5mm ceramic ferrule. FC connectors provide excellent mechanical stability and are often used in high-vibration environments or test equipment applications.
- MTP/MPO Connector: The MTP/MPO (Multi-Fiber Push-On/Pull-Off) connector is designed to accommodate multiple fibers in a single connector. It features a rectangular-shaped ferrule with a push-pull latching mechanism. MTP/MPO connectors are commonly used in high-density applications like data centers and backbone networks.
- MT-RJ Connector: The MT-RJ (Mechanical Transfer-Registered Jack) is a duplex connector that combines both fiber strands into a single RJ-style housing. It is used primarily for multimode applications and provides a compact and space-saving solution.
- E2000 Connector: The E2000 connector is a small form-factor connector known for its high performance and reliability. It features a push-pull mechanism with a spring-loaded shutter to protect the ferrule from contamination. E2000 connectors are widely used in telecommunications, data centers, and high-speed optical networks.
- MU Connector: The MU (Miniature Unit) connector is a small form-factor connector similar in size to the SC connector but with a 1.25mm ferrule. It provides high-density connectivity and is commonly used in data centers, LANs, and telecommunication networks.
- LX.5 Connector: The LX.5 connector is a duplex connector designed for high-performance applications, especially in long-haul telecom networks. It features a compact design and offers low insertion loss and excellent return loss performance.
- DIN Connector: The DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) connector is commonly used in European telecommunications networks. It features a screw-on design and is known for its robustness and high mechanical stability.
- SMA Connector: The SMA (SubMiniature version A) connector is commonly used in RF and microwave applications. It features a threaded coupling mechanism and a 3.175mm ferrule with a screw-on design. SMA connectors are used in specific applications such as fiber-optic sensors or high-frequency devices.
- LC TAB Uniboot Connector: The LC TAB (Tape-Aided Bonding) uniboot connector combines the LC connector design with a unique tab feature. It allows for the easy polarity reversal of fiber connections without the need for additional tools or cable management. LC TAB uniboot connectors are commonly used in data centers and high-density applications where polarity management is required.
- What is the difference between fiber cable and fiber patch cord?
-
Fiber patch cords and fiber cables are crucial components in fiber optic networks, serving different purposes and catering to specific requirements. Understanding the distinctions between these two elements is essential for selecting the appropriate solution for network installations. In the following comparison table, we outline the key differences between fiber patch cords and fiber cables, including structure and length, purpose, installation, connector types, fiber type, flexibility, and application.
Comparing Item
Fiber Patch Cords
Fiber Cables
Explanation
Structure and Length
Shorter; designed for localized connections
Longer; used for long-distance transmission
Fiber patch cords are shorter in length, typically a few meters, and are designed for connecting devices within a limited distance range. Fiber cables, on the other hand, are longer and used to establish main communication links spanning hundreds or thousands of meters.
Purpose
Connect specific devices within a localized area
Establish main communication links between different locations or network segments
Fiber patch cords serve the purpose of connecting specific devices or equipment within a localized area or network. Fiber cables, in contrast, are used to establish the primary communication link between different locations or network segments.
Installation
Easily installed or replaced by plugging/unplugging
Requires professional installation (e.g., burying underground, stringing between poles)
Fiber patch cords are readily available and can be easily installed or replaced by simply plugging or unplugging them from devices. Fiber cables, however, require professional installation, such as burying underground or stringing between poles.
Connector Types
Compatible connectors (e.g., LC, SC, MTP/MPO)
Connectors specific to the installation (e.g., SC, LC, ST)
Fiber patch cords commonly use connectors that are compatible with the devices they connect, such as LC, SC, or MTP/MPO connectors. Fiber cables, on the other hand, often terminate with connectors specific to the installation, such as SC, LC, or ST connectors.
Fiber Type
Single-mode or multi-mode variants, depending on requirement
Single-mode or multi-mode variants, depending on requirement
Both fiber patch cords and fiber cables are available in single-mode or multi-mode variants, and the specific type is selected based on the required transmission distance and the devices being connected.
Flexibility
More flexible for easy maneuverability
Less flexible due to larger diameter and protective jackets
Fiber patch cords are more flexible, allowing for easy maneuverability and connections in tight spaces or corners. In contrast, fiber cables are less flexible due to their larger diameter and protective jackets.
Application
Used for network equipment connections or localized connections
Used for long-range telecommunications, internet backbone, or trunk lines
Fiber patch cords are primarily used for network equipment connections, patch panels, or interconnecting devices within a localized area or data center. Fiber cables are commonly used for long-range telecommunications or backbone connections.
Understanding the differences between fiber patch cords and fiber cables is crucial for network design and installation. While fiber cables are primarily used for establishing long-distance communication links, fiber patch cords play a vital role in connecting devices within a localized area. Each component serves a specific purpose and requires different installation methods. By selecting the appropriate connector types, fiber types, and considering factors such as flexibility and application, one can ensure efficient and reliable data transmission in fiber optic networks.
- What color is a fiber optic patch cord?
-
Fiber optic patch cords can come in various colors depending on the manufacturer, industry standards, and specific applications. Here are some common colors used for fiber optic patch cords:
- Orange: Orange is the most widely used color for single-mode fiber optic patch cords. It has become an industry standard for identifying single-mode connections.
- Aqua: Aqua is commonly used for multi-mode fiber optic patch cords, specifically those designed for high-speed applications such as 10 Gigabit Ethernet or higher. It helps differentiate them from single-mode patch cords.
- Yellow: Yellow is sometimes used for both single-mode and multi-mode fiber optic patch cords. However, it is less common than orange or aqua and may vary depending on the manufacturer or specific application.
- Other Colors: In some cases, fiber optic patch cords may come in different colors, such as green, blue, red, or black. These colors may be used to denote specific applications, network classifications, or for aesthetic purposes. However, it's important to note that color coding can vary among different manufacturers or regions.
The color of a fiber optic patch cord primarily serves as a visual indication to help distinguish between different fiber types, modes, or applications. It is recommended to refer to industry standards or labeling provided by the manufacturer to ensure accurate identification and proper usage.
- What are the specifications to consider when purchasing a fiber patch cord?
-
When considering the purchase of a fiber patch cord, understanding its specifications is crucial to ensure compatibility, performance, and reliability in your network infrastructure. The following table provides a comprehensive overview of important specifications to consider, including cable size, type, fiber characteristics, connector type, jacket material, operating temperature, tensile strength, bend radius, insertion loss, return loss, and the availability of a pulling eye.
Specification
Description
Cable Size
Typically available in diameters of 2mm, 3mm, or 3.5mm.
Cable Type
Can be simplex (single fiber) or duplex (dual fibers in a single cable).
Fiber Type
Single-mode or multi-mode, depending on the intended application and transmission distance.
Fiber Diameter
Commonly available in 9/125µm (single-mode) or 50/125µm or 62.5/125µm (multi-mode) options.
Connector Type
Various connector types such as LC, SC, ST, or MTP/MPO, depending on the specific application.
Cable Jacket Material
Typically made of PVC (polyvinyl chloride), LSZH (low smoke zero halogen), or plenum-rated material for different environmental requirements.
Operating Temperature
Range of temperatures at which the patch cord can function optimally, such as -20°C to 70°C.
Tensile Strength
The maximum force or load a patch cord can withstand without breaking, usually measured in pounds or newtons.
Bend Radius
The minimum radius at which a patch cord can be bent without causing excessive signal loss, typically measured in millimeters.
Insertion Loss
The amount of optical power lost when the patch cord is connected, usually measured in decibels (dB).
Return Loss
The amount of light reflected back towards the source due to signal loss, typically measured in decibels (dB).
Pulling Eye
Optional feature with a grip attached to the cable for easier installation and removal.
Considering the specifications of a fiber patch cord is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. Factors such as cable size, type, fiber characteristics, connector type, jacket material, operating temperature, tensile strength, bend radius, insertion loss, return loss, and the availability of a pulling eye directly impact performance and reliability in different network environments. By carefully evaluating these specifications, you can select the most suitable fiber patch cord to meet your specific requirements and ensure efficient data transmission in your fiber optic network.
- What are common terminologies related to fiber patch cords?
-
To navigate the world of fiber patch cords, it is essential to understand the common terminologies associated with them. These terminologies encompass connector types, fiber types, connector polishing, fiber configurations, and other important aspects that play a crucial role in selecting and using fiber patch cords effectively. In the following table, we provide a comprehensive overview of these terminologies along with detailed explanations, helping you build a solid foundation of knowledge in this domain.
Connector Types:
- FC (Ferrule Connector): FC connectors feature a screw-on coupling mechanism and are commonly used in telecommunication and test environments. They have a typical ferrule diameter of 2.5mm.
- LC (Lucent Connector): LC connectors have a push-pull design and are widely used in high-density environments. They provide low insertion loss and are suitable for data centers, LANs, and fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) applications. LC connectors typically have a ferrule diameter of 1.25mm.
- SC (Subscriber Connector): SC connectors feature a push-pull coupling mechanism. They are commonly used in LANs, patch panels, and equipment connections due to their ease of installation and reliable performance. SC connectors typically have a ferrule diameter of 2.5mm.
- ST (Straight Tip): ST connectors use a bayonet-style coupling mechanism and are often employed in multimode networks such as LANs and premises cabling. They typically have a ferrule diameter of 2.5mm.
- MTP/MPO (Multi-Fiber Push-On/Pull-Off): MTP/MPO connectors are used for high-density applications, providing multiple fibers within a single connector. They are commonly used in data centers and backbone networks. The number of fibers per connector can be 12 or 24.
- MT-RJ (Mechanical Transfer-Registered Jack): MT-RJ connectors are duplex connectors that combine both fiber strands into a single RJ-style housing. They are commonly used for multimode applications and provide a space-saving solution.
- E2000 Connector: The E2000 connector is a small form-factor connector known for its high performance and reliability. It features a push-pull mechanism with a spring-loaded shutter to protect the ferrule from contamination. E2000 connectors are widely used in telecommunications, data centers, and high-speed optical networks.
- MU (Miniature Unit) Connector: The MU connector is a small form-factor connector similar in size to the SC connector but with a 1.25mm ferrule. It provides high-density connectivity and is commonly used in data centers, LANs, and telecommunication networks.
- LX.5 Connector: The LX.5 connector is a duplex connector designed for high-performance applications, especially in long-haul telecom networks. It features a compact design and offers low insertion loss and excellent return loss performance.
Fiber Types:
- Single-mode fiber: Single-mode fiber is specifically designed for long-distance communication, featuring a narrow core diameter of 9/125µm that allows the transmission of a single mode of light, enabling high bandwidth and longer transmission distances. For single-mode fiber patch cords, there are two designations to consider: OS1 (Optical Single-Mode 1) and OS2 (Optical Single-Mode 2). OS1 is optimized for indoor use, exhibiting lower attenuation and suitable for various indoor networking applications. On the other hand, OS2 is specifically designed for outdoor and longer-distance applications where greater signal reach is required. With these designations, fiber patch cord users can select the appropriate single-mode fiber patch cords based on their specific application requirements and transmission distances.
- Multi-mode fiber: Multi-mode fiber is specifically designed for shorter distance applications, characterized by a larger core diameter, such as 50/125µm or 62.5/125µm. It enables the transmission of multiple light modes simultaneously, providing lower bandwidth and shorter transmission distances compared to single-mode fiber. For multi-mode fiber patch cords, different grades are designated to indicate their performance characteristics. These grades include OM1 (Optical Multimode 1), OM2 (Optical Multimode 2), OM3 (Optical Multimode 3), OM4 (Optical Multimode 4), and OM5 (Optical Multimode 5). These designations are based on the fiber type and the modal bandwidth, which impact the transmission distance and data rate capabilities. OM1 and OM2 are older multi-mode grades, typically used in legacy installations, while OM3, OM4, and OM5 support higher data rates over longer distances. The choice of multimode fiber patch cords depends on the specific requirements of the network, considering factors such as data rate, distance, and budget constraints.
Fiber Configuration:
- Simplex: Simplex patch cords consist of a single fiber, making them suitable for point-to-point connections where only one fiber is required.
- Duplex: Duplex patch cords contain two fibers within a single cable, allowing for bidirectional communication. They are commonly used for applications where simultaneous transmit and receive functionality is needed.
Connector Polishing:
- APC (Angled Physical Contact): APC connectors feature a slight angle on the fiber endface, reducing back reflections and providing excellent return loss performance. They are commonly used in applications where low return loss is crucial, such as in high-speed networks or long-distance communications.
- UPC (Ultra Physical Contact): UPC connectors have a flat, smooth fiber endface, providing low insertion loss and high return loss performance. They are widely used in various fiber optic applications, including telecommunications and data centers.
Other Specifications
- Patch Cord Length: Patch cord length refers to the overall length of the fiber patch cord, typically measured in meters or feet. The length can vary based on specific requirements, such as the distance between devices or the layout of the network.
- Insertion Loss: Insertion loss refers to the amount of optical power lost when the fiber patch cord is connected. It is typically measured in decibels (dB). Lower insertion loss values indicate better signal transmission and higher efficiency of the fiber connection.
- Return Loss: Return loss refers to the amount of light reflected back towards the source due to signal loss in the fiber patch cord. It is typically measured in decibels (dB). Higher return loss values indicate better signal quality and lower signal reflections.
- Pulling Eye: A pulling eye is an optional feature with a grip attached to the fiber patch cord. It facilitates easier installation, removal, and handling of the patch cord, especially in tight spaces or when dealing with multiple patch cords.
- Jacket Material: Jacket material refers to the outer protective covering of the fiber patch cord. Common materials used for the jacket include PVC (polyvinyl chloride), LSZH (low smoke zero halogen), or plenum-rated material. The choice of jacket material depends on factors such as flexibility, flame resistance, and environmental considerations.
- Bend Radius: Bend radius refers to the minimum radius at which the fiber patch cord can be bent without causing excessive signal loss. It is typically measured in millimeters and is specified by the manufacturer. Adhering to the recommended bend radius helps maintain optimal signal integrity and prevent signal degradation.
Gaining familiarity with the terminologies associated with fiber patch cords is crucial for effectively understanding, selecting, and utilizing these components in various networking applications. The connector types, fiber types, configurations, polishing methods, etc. are key factors to consider. Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently engage in discussions, make informed decisions, and ensure efficient and reliable data transmission through fiber patch cords in your network infrastructure.
- How many types of fiber patch cord polishing exist?
-
There are two main types of fiber patch cord polishing commonly used in the industry:
- APC (Angled Physical Contact) Polishing: APC polishing involves polishing the fiber endface at an angle of typically 8 degrees. The angled endface helps to minimize back reflections, resulting in low return loss and improved signal performance. APC connectors are commonly used in applications where low return loss is critical, such as in high-speed networks or long-distance communications.
- UPC (Ultra Physical Contact) Polishing: UPC polishing involves polishing the fiber endface perpendicularly, resulting in a flat and smooth surface. UPC connectors provide low insertion loss and high return loss performance. They are widely used in various fiber optic applications, including telecommunications, data centers, and local area networks.
The choice between APC and UPC polishing depends on the specific requirements and applications. APC connectors are typically used in applications where low return loss and high signal quality are of utmost importance, such as in long-haul networks or systems utilizing wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology. UPC connectors are more commonly used in general-purpose applications and environments where low insertion loss and high reliability are crucial.
It's important to note that the choice of polishing type should align with the corresponding connector type and the specific requirements of the network and equipment being used.
- What is a fiber optic patch cord used for?.
-
A fiber optic patch cord, also known as a fiber optic jumper or fiber optic patch cable, is used for establishing a temporary or permanent fiber optic connection between two devices or network components. These patch cords play a vital role in the transmission of data, voice, and video signals in fiber optic networks. Here are some common uses for fiber optic patch cords:
- Device Connections: Fiber patch cords are widely used to connect various devices in network installations, such as switches, routers, servers, media converters, and optical transceivers. They provide a reliable and high-speed connection, ensuring efficient data transmission between network components.
- Patch Panel Connections: Fiber patch cords are used to establish connections between active equipment and patch panels in data centers or telecommunications rooms. They allow for flexibility in managing network connections, facilitating easy moves, adds, and changes.
- Cross-Connects and Interconnects: Fiber patch cords are used to create cross-connections and interconnections between different fiber optic cables or systems. They provide a means to connect different network segments or separate fiber optic systems for seamless communication.
- Fiber Optic Testing and Troubleshooting: Fiber optic patch cords are essential for testing and troubleshooting fiber optic links. They are used in conjunction with testing equipment to measure optical power levels, verify signal integrity, and identify any issues or faults in the fiber optic network.
- Fiber Optic Distribution Frames/Boxes: Fiber patch cords are utilized in fiber optic distribution frames or boxes to establish connections between incoming and outgoing fibers. They enable the distribution of signals to the appropriate destinations within the fiber optic infrastructure.
Overall, fiber optic patch cords are indispensable components in fiber optic networks. They provide the necessary connectivity to ensure efficient and reliable data transmission, support network flexibility and scalability, and enable seamless communication between various devices and network components.
- What are the pros and cons of fiber patch cords compared to copper cables?
-
Fiber patch cords offer several advantages over copper cables, but they also have a few limitations. Here are the pros and cons of fiber patch cords compared to copper cables:
Pros of Fiber Patch Cords:
- High Bandwidth: Fiber optic cables have a much higher bandwidth capacity compared to copper cables. They can transmit data at significantly faster speeds, making them suitable for applications that require high data rates.
- Long Transmission Distance: Fiber patch cords can transmit data over longer distances without significant signal degradation. Single-mode fiber can transmit data for several kilometers without the need for signal regeneration.
- Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference since they use light signals instead of electrical signals. This makes them ideal for environments with high levels of electromagnetic noise, such as industrial settings or areas with heavy electrical equipment.
- Security: Fiber optic cables do not emit electromagnetic signals, making them difficult to tap into or intercept. This enhances security and protects transmitted data from unauthorized access or eavesdropping.
- Lightweight and Compact: Fiber patch cords are thinner and lighter than copper cables. This makes them easier to install, handle, and manage within network infrastructure.
Cons of Fiber Patch Cords:
- Higher Cost: Fiber optic cables and associated equipment tend to be more expensive than copper cables. The initial investment for fiber optic infrastructure can be higher, which may be a consideration in budget-limited scenarios.
- Fragility: Fiber optic cables are more delicate than copper cables and can be prone to bending or breaking if mishandled or improperly installed. Special care must be taken during installation and maintenance to prevent damage.
- Limited Availability of Equipment: In some cases, fiber optic equipment or components may be less readily available compared to copper-based alternatives. This can lead to longer lead times or a more limited selection of compatible devices in certain regions.
- Skill Requirements: Fiber optic installation and maintenance require specialized knowledge and skills. The complexity involved may necessitate trained technicians or additional expertise, potentially increasing operational costs.
- Limited Power Transmission: Unlike copper cables, fiber optic cables cannot transmit electrical power. Separate power cables or alternative power transmission methods must be used alongside fiber optic cables when power delivery is required.
It is important to carefully assess the specific requirements and constraints of the network to determine whether fiber patch cords or copper cables are more suitable for a particular application. Factors such as data speed, transmission distance, environmental conditions, security concerns, and budget constraints should be considered when making a decision.
- How are you?
- I am fine
CONTACT US

FMUSER INTERNATIONAL GROUP LIMITED.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
If you would like to keep touch with us directly, please go to contact us












